The treatment for gynecologic cancers often includes a hysterectomy – a partial or full removal of a woman’s reproductive organs. A full hysterectomy removes the cervix and uterus plus often the ovaries and fallopian tubes. A partial hysterectomy removes the uterus but leaves the other organs intact. This surgery can be performed using one of several techniques. Your Minnesota Oncology Gynecologic Oncologist will talk with you about the team’s recommendation for your specific surgery needs.
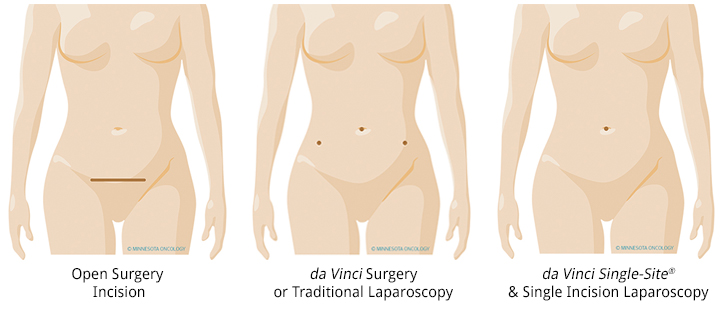
- Open Surgery requires an incision large enough for the doctor to reach inside and touch the organs.
- Laparascopic Surgery requires only a few small incisions. The surgeon operates through using long instruments and a tiny camera. The camera sends images to a video monitor in the operating room to guide the surgeon during the procedure.
- da Vinci Surgery, which is also minimally invasive, includes a more advanced set of instruments for the surgeon to see and control the surgery. The surgeon is able to see inside your abdomen in 3-D with high-definition clarity. S/He then uses special instruments attached to their wrists which bend and rotate far greater than the human hand.
This diagram compares the incisions that are made for the various types of hysterectomy surgery.
Whether a full or partial hysterectomy is recommended the da Vinci Surgery System is often considered because of the minimal scarring and reduced risk for blood loss.
Surgery Outcomes
Here are some of the positive outcomes for cancer patients when using da Vinci Surgery over open surgery or laparascopic surgery to perform a hysterectomy.
da Vinci Surgery compared to open surgery:
- Lower complication rate1,2,3,4
- Less need for narcotics after the surgery3,4
- Shorter hospital stay1,2,3,4,5
- Less blood loss and less likelihood for transfusion1,2,3,4,5
da Vinci Surgery compared to traditional laparoscopy:
- Shorter hospital stay6,7,8
- Less blood loss6,7,8,10,11
- Less chance of changing procedure to open surgery7,9,12
1 Elsahwi, Karim S. et al. “Comparison between 155 Cases of Robotic vs. 150 Cases of Open Surgical Staging for Endometrial Cancer.” Gynecologic Oncology 124.2 (2012): 260-64. Print. 2 Pant, A. et al. “Robotic Surgery Compared with Laparotomy for High-grade Endometrial Cancer.” Journal of Robotic Surgery 8.2 (2014): 163-67. Print. 3 Halliday, D. et al. “Robotic Radical Hysterectomy: Comparison of Outcomes and Cost.” Journal of Robotic Surgery 4.4 (2010): 211-16. Print. 4 Estape, R. et al. “A Case Matched Analysis of Robotic Radical Hysterectomy with Lymphadenectomy Compared with Laparoscopy and Laparotomy.” Gynecologic Oncology 113.3 (2009): 357-61. Print. 5 Feuer, G. et al. “Robotic Surgery for Staging of Serous Papillary and Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Endometrium.” The International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery 10.3 (2014): 306-13. Print. 6 Reza, M. et al. “Meta-analysis of Observational Studies on the Safety and Effectiveness of Robotic Gynaecological Surgery.” British Journal of Surgery 97.12 (2010): 1772-783. Print. 7 Lim, P. et al. “A Comparative Detail Analysis of the Learning Curve and Surgical Outcome for Robotic Hysterectomy with Lymphadenectomy versus Laparoscopic Hysterectomy with Lymphadenectomy in Treatment of Endometrial Cancer: A Case-matched Controlled Study of the First One Hundred Twenty Two Patients.” Gynecologic Oncology 120.3 (2011): 413- 18. Print. 8 Magrina, J. et al. “Robotic Radical Hysterectomy: Comparison with Laparoscopy and Laparotomy.” Gynecologic Oncology 109.1 (2008): 86-91. Print. 9 Magrina, J. F. et al. “Robotic Surgery for Endometrial Cancer: Comparison of Perioperative Outcomes and Recurrence with Laparoscopy, Vaginal/laparoscoy and Laparotomy.” European Journal of Gynaecological Oncology XXXII.5 (2011): 476-80. Print. 10 Smith, A. et al. “Dual-console Robotic Surgery Compared to Laparoscopic Surgery with Respect to Surgical Outcomes in a Gynecologic Oncology Fellowship Program.” Gynecologic Oncology 126.3 (2012): 432- 36. Print. 11 Ran, Longke et al. “Comparison of Robotic Surgery with Laparoscopy and Laparotomy for Treatment of Endometrial Cancer: A MetaAnalysis.” Ed. Shannon M. Hawkins. PLoS ONE 9.9 (2014): e108361. PMC. Web. 18 Feb. 2015. 12 Available from: www.womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/factsheet/hysterectomy.pdf.