Lung Cancer is the leading cause of all cancer deaths in the United States. It is estimated that over 228,190 new cases will be diagnosed and approximately 159,480 people will die from lung cancer this year. More people die from lung cancer than breast, colon and prostate cancers combined. Although lung cancer is the deadliest cancer type, it is rare in people under the age of 40.
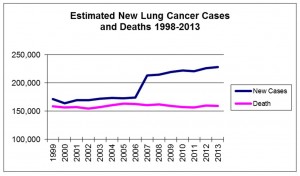
Data pulled from the American Cancer Society, Cancer Facts and Figures 1998-2013 – July 2013.
There are two types of lung cancer: non-small cell and small cell.
- Non-small cell – Almost 85% of all lung cancer is non-small cell. It can spread quickly and can be found near the bronchus, lung and outer lung.
- Small cell – Nearly 15% of all lung cancer is small cell. The cancer cells are found in the bronchi, center of the chest, multiply quickly and form large tumors that spread throughout the body. This type of cancer is almost always caused by smoking.
Risk Factors
- Smoking – the leading cause of lung cancer. Tobacco smoke causes more than eight out of 10 lung cancer cases. This includes marijuana, as many of the cancer-causing substances in tobacco are also found in marijuana.
- Exposure – being exposed to arsenic, asbestos, radon, uranium, beryllium, vinyl chloride, nickel chromates, coal products, mustard gas, chloromethyl ethers, gasoline and diesel exhaust can also increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Disease – certain diseases, such as silicosis and berylliosis, can increase the chances of lung cancer.
- Family history – the chance of developing lung cancer rises when immediate family members have the disease.
- Radiation Treatment to Lungs – People who have had radiation to the chest to treat another cancer are at higher risk for lung cancer, especially if they smoke.
- Air pollution – living in some cities with strong air pollution may increase the chances of lung cancer.
- Diet – a diet with low volumes of fruit and vegetables may increase the risk of lung cancer in people who are exposed to tobacco.
Signs and Symptoms
Most lung cancers do not cause symptoms until the cancer has spread. However, many of the symptoms listed below should be addressed by a doctor immediately:
- A cough that does not go away
- Chest pain, made worse by deep breathing, coughing or laughing
- Hoarseness
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Bloody or rust colored sputum (spit or phlegm)
- New onset of wheezing, or shortness of breath
- Reoccurring infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia
Screening
Currently, there are no tests available that can detect lung cancer at an early stage. Often, the cancer has spread into other areas of the body by the time it is detected. New technology is being researched and developed to better identify lung cancer in its early stages.
Staging
If cancer is found, a physician will need to determine the progression of the cancer. This classification, called staging, allows the healthcare provider to properly identify a treatment plan and to determine the prognosis. All cancers are staged on a roman numeral scale, of I-IV (1-4), where the higher stage represents more advanced cancer.
Treatment
There are many treatment options for lung cancer, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery. Each method may be used alone, or in combination.
- Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs are administered orally or infused directly into the bloodstream. They travel throughout the body reaching cancer cells that may have spread into other areas of the body outside the lungs.
- Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy rays to kill cancer cells in the treatment area. It is primarily administered from a machine outside the body.
- Surgery treats the cancer by removing the cancerous tissue. The type of surgery required depends on the stage of the cancer.
- Wedge Resection – involves removing a section of the lobe; a part of the lung.
- Lobectomy – involves removing the entire lobe.
- Pneumonectomy – involves the removal of the entire lung and lymph nodes.