Lung cancer staging is the assessment of the extent to which lung cancer has spread from its original source.
Lung cancer stages and symptoms aid in determining treatment. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease, which assists the doctor in understanding the seriousness of the cancer, providing an optimal treatment plan, identifying potential clinical trials for viable treatment options, and even providing chances of survival (prognosis).
The staging system most often used for lung cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM system, which is based on 3 key pieces of information:
- The size and extent of the main tumor (T)
- The spread to nearby (regional) lymph nodes (N)
- The spread (metastasis) (M) to other organs of the body
After determining a diagnosis of small cell (SCLC) or non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), additional testing determines if the cancer cells have spread (metastasized) within the chest or to other parts of the body. Information gathered determines the stage of the disease and the treatment plan.
Small cell lung cancer falls under one of two categories: limited and extensive.
In limited-stage small cell lung cancer, cancer is found in one lung, the tissues between the lungs, and nearby lymph nodes only. Alternatively, extensive-stage small cell lung cancer has spread outside of the lung in which it began or to other parts of the body.
Additional tests and procedures that may be used in the small cell lung cancer staging process include:
- Laboratory tests
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: The removal of bone marrow, blood, and a small piece of bone by inserting a hollow needle into the hipbone or breastbone. A pathologist views the bone marrow, blood, and bone under a microscope to look for signs of cancer.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
- Lymph node biopsy: The removal of all or part of a lymph node. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
- Radionuclide bone scan
- Occult (hidden) cancer: The main tumor can’t be assessed for some reason, or cancer cells are seen in a sample of sputum or other lung fluids, but the cancer isn’t found with other tests, so its location can’t be determined (TX). The cancer is not thought to have spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant parts of the body (M0).
- Stage 0: The tumor is found only in the top layers of cells lining the air passages, but it has not invaded deeper into other lung tissues (Tis). The cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant parts of the body (M0).
- Stage I: Stage I is divided into stages IA and IB:
- Stage IA: The tumor is in the lung only and is 3 centimeters or smaller.
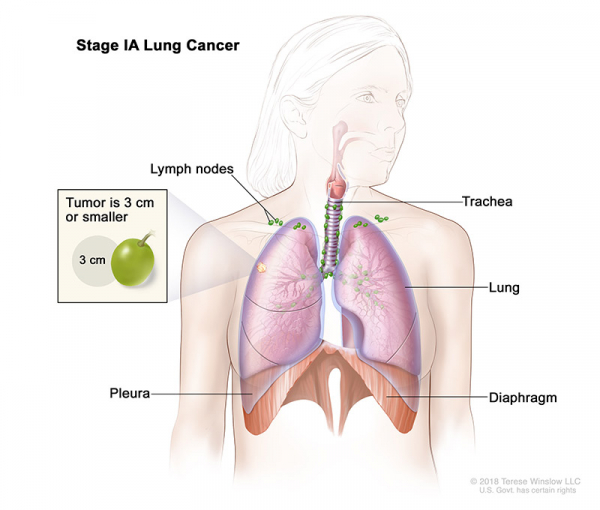
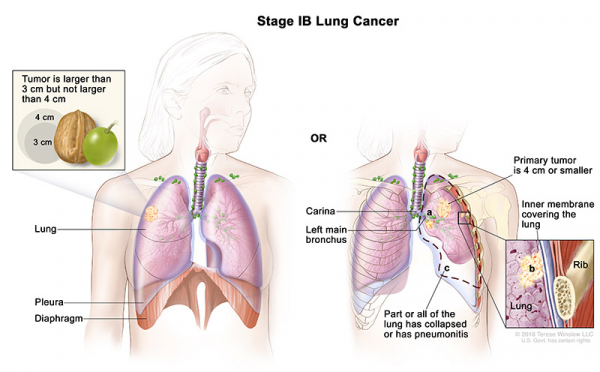
- Stage IB: The cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or to distant parts of the body. The tumor has one or more of the following features:
- It is larger than 3 cm but not larger than 4 cm across.
- It has grown into a main bronchus, but is not within 2 cm of the carina (the point where the windpipe splits into the left and right main bronchi) and it is not larger than 4 cm across.
- It has grown into the visceral pleura (the membranes surrounding the lungs) and is not larger than 4 cm across.
- It is partially clogging the airways (and is not larger than 4 cm across).
- Stage IA: The tumor is in the lung only and is 3 centimeters or smaller.
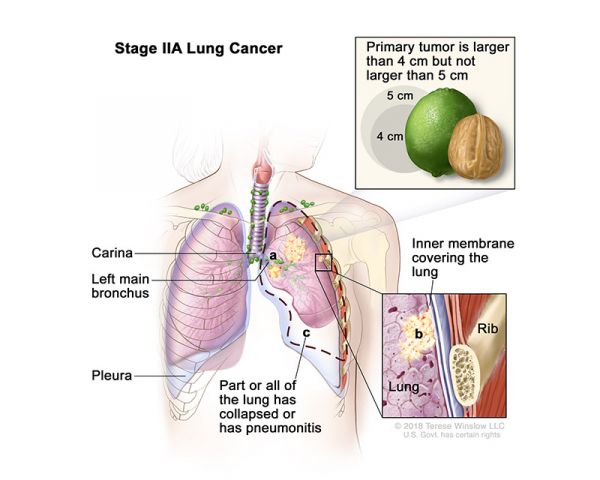
- Stage II: Stage II is divided into stages IIA and IIB:
- Stage IIA: The tumor is larger than 4 centimeters but not larger than 5 centimeters or smaller and cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the tumor.
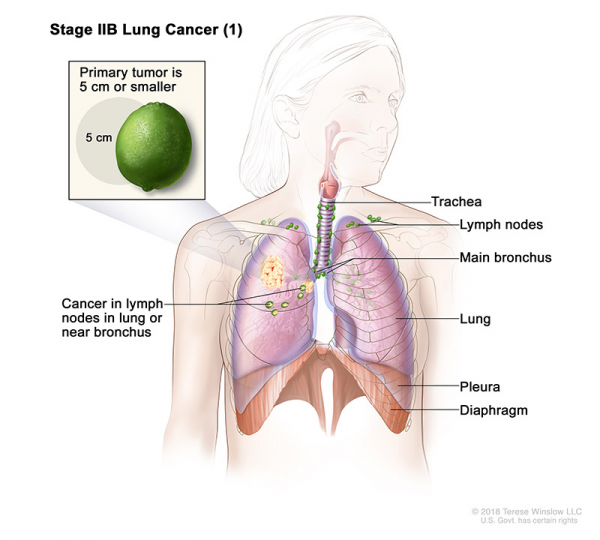
- Stage IIB (1): The tumor is 5 centimeters or smaller and cancer has spread to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor. The lymph nodes with cancer are in the lung or near the bronchus. Also, one or more of the following may be found:
- Cancer has spread to the main bronchus, but has not spread to the carina.
- Cancer has spread to the innermost layer of the membrane that covers the lung.
- Part of the lung or the whole lung has collapsed or has developed pneumonitis.
OR
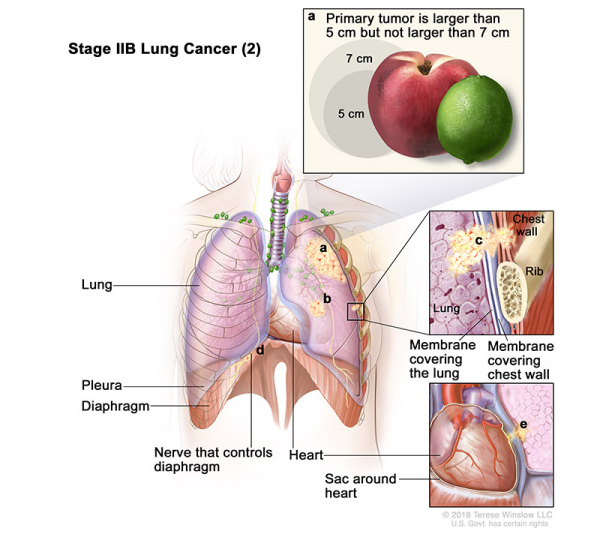
- Stage IIB (2): Cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes and one or more of the following is found:
- The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters but not larger than 7 centimeters.
- There are one or more separate tumors in the same lobe of the lung as the primary tumor.
- Cancer has spread to any of the following:
- The membrane that lines the inside of the chest wall.
- Chest wall.
- The nerve that controls the diaphragm.
- Outer layer of tissue of the sac around the heart.
- Stage IIA: The tumor is larger than 4 centimeters but not larger than 5 centimeters or smaller and cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the tumor.
- Stage III: Stage III is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, IIIC
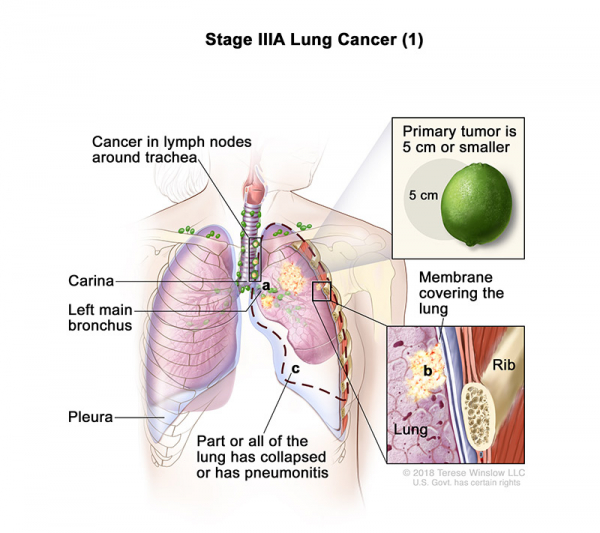
- Stage IIIA (1): The tumor is 5 centimeters or smaller and cancer has spread to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor. The lymph nodes with cancer are around the trachea or aorta, or where the trachea divides into the bronchi. Also, one or more of the following may be found:
- Cancer has spread to the main bronchus, but has not spread to the carina.
- Cancer has spread to the innermost layer of the membrane that covers the lung.
- Part of the lung or the whole lung has collapsed or has developed pneumonitis.
OR
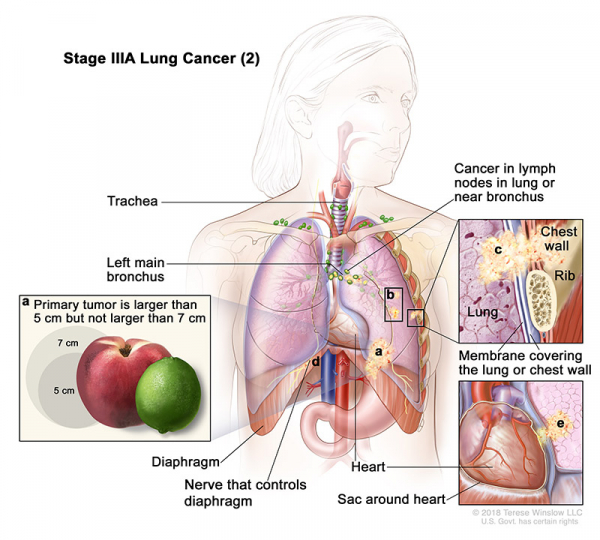
- Stage IIIA (2): Cancer has spread to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor. The lymph nodes with cancer are in the lung or near the bronchus. Also, one or more of the following is found:
- The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters but not larger than 7 centimeters.
- There are one or more separate tumors in the same lobe of the lung as the primary tumor.
- Cancer has spread to any of the following:
- The membrane that lines the inside of the chest wall.
- The nerve that controls the diaphragm.
- Outer layer of tissue of the sac around the heart.
OR
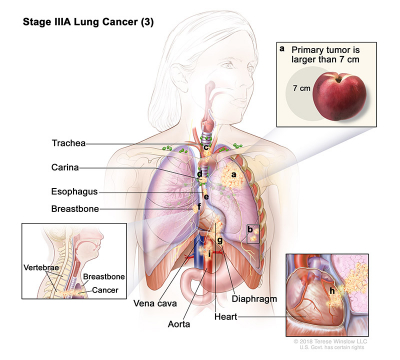
- Stage IIIA (3): Cancer may have spread to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor. The lymph nodes with cancer are in the lung or near the bronchus. Also, one or more of the following is found:
- The tumor is larger than 7 centimeters.
- There are one or more separate tumors in a different lobe of the lung with the primary tumor.
- The tumor is any size and cancer has spread to any of the following:
- Trachea.
- Carina.
- Esophagus.
- Breastbone or backbone.
- Diaphragm.
- Heart.
- Major blood vessels that lead to or from the heart (aorta or vena cava).
- Nerve that controls the larynx (voice box).
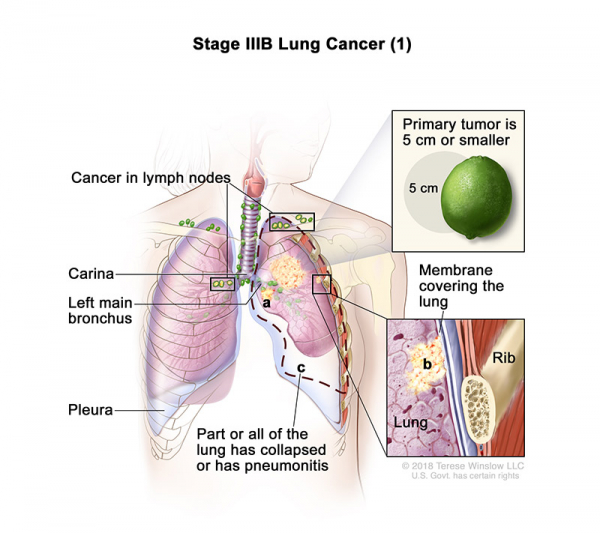
- Stage IIIB (1): The tumor is 5 centimeters or smaller and cancer has spread to lymph nodes above the collarbone on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor or to any lymph nodes on the opposite side of the chest as the primary tumor. Also, one or more of the following may be found:
- Cancer has spread to the main bronchus, but has not spread to the carina.
- Cancer has spread to the innermost layer of the membrane that covers the lung.
- Part of the lung or the whole lung has collapsed or has developed pneumonitis.
OR
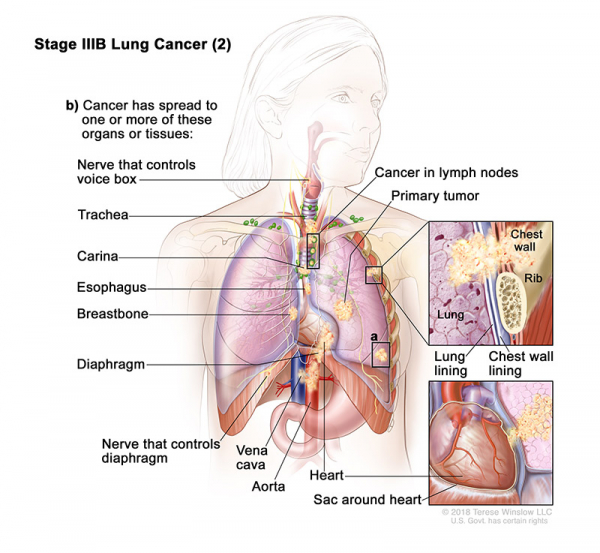
- Stage IIIB (2): The tumor may be any size and cancer has spread to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor. The lymph nodes with cancer are around the trachea or aorta, or where the trachea divides into the bronchi. Also, one or more of the following is found:
- There are one or more separate tumors in the same lobe or a different lobe of the lung with the primary tumor.
- Cancer has spread to any of the following:
- The membrane that lines the inside of the chest wall.
- Chest wall.
- The nerve that controls the diaphragm.
- Outer layer of tissue of the sac around the heart.
- Trachea.
- Carina.
- Esophagus.
- Breastbone or backbone.
- Diaphragm.
- Heart.
- Major blood vessels that lead to or from the heart (aorta or vena cava).
- Nerve that controls the larynx (voice box).
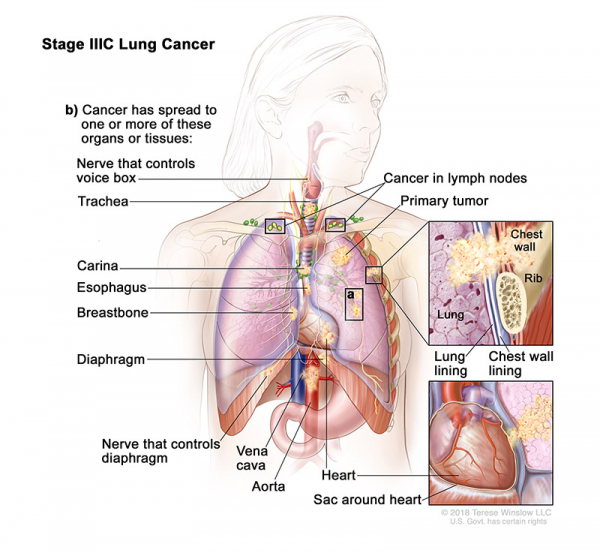
- Stage IIIC: The tumor may be any size and cancer has spread to lymph nodes above the collarbone on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor or to any lymph nodes on the opposite side of the chest as the primary tumor. Also, one or more of the following is found:
- There are one or more separate tumors in the same lobe or a different lobe of the lung with the primary tumor.
- Cancer has spread to any of the following:
- The membrane that lines the inside of the chest wall.
- Chest wall.
- The nerve that controls the diaphragm.
- Outer layer of tissue of the sac around the heart.
- Trachea.
- Carina.
- Esophagus.
- Breastbone or backbone.
- Diaphragm.
- Heart.
- Major blood vessels that lead to or from the heart (aorta or vena cava).
- Nerve that controls the larynx (voice box).
- Stage IIIA (1): The tumor is 5 centimeters or smaller and cancer has spread to lymph nodes on the same side of the chest as the primary tumor. The lymph nodes with cancer are around the trachea or aorta, or where the trachea divides into the bronchi. Also, one or more of the following may be found:
- Stage IV: Stage IV is divided into stages IVA and IVB.
- Stage IVA: The tumor may be any size and cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes. One or more of the following is found:
- There are one or more tumors in the lung that does not have the primary tumor.
- Cancer is found in the lining around the lungs or the sac around the heart.
- Cancer is found in fluid around the lungs or the heart.
- Cancer has spread to one place in an organ not near the lung, such as the brain, liver, adrenal gland, kidney, bone, or to a lymph node that is not near the lung.
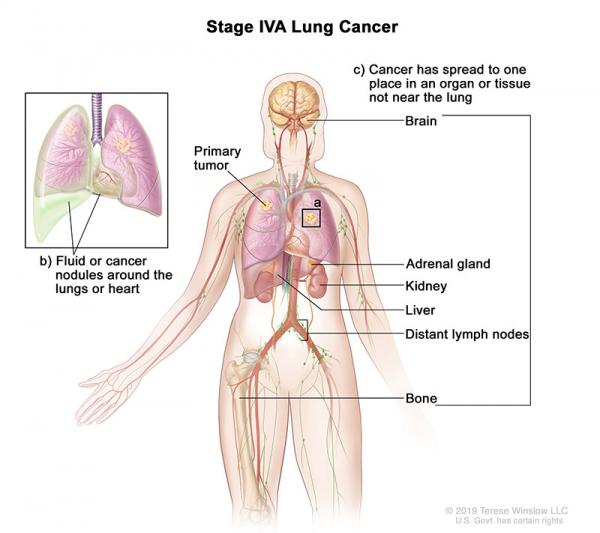
- Stage IVB: Cancer has spread to multiple places in one or more organs that are not near the lung.
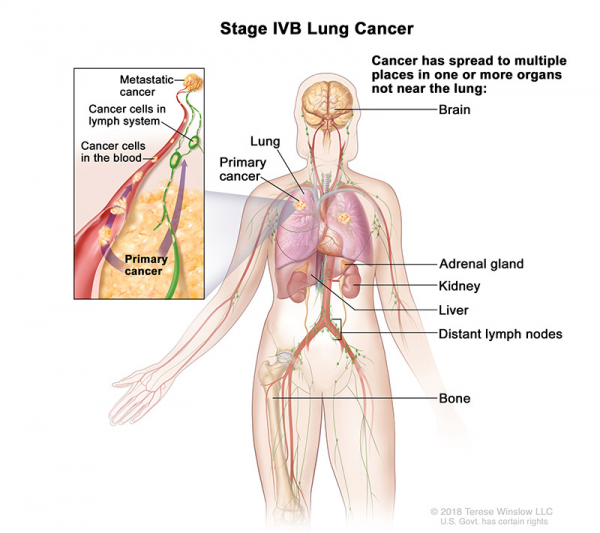
- Stage IVA: The tumor may be any size and cancer may have spread to the lymph nodes. One or more of the following is found: